 “Take roses fresh from the flower bed, strip off the leaves, remove the white from the petals and put them in the mortar; pour over some fish sauce and rub fine. Add a glass of fish sauce and strain the juice through the colander. This done, take four cooked calf’s brains, skin them and remove the nerves; crush eight scruples of pepper moistened with the juice and rub with the brains; thereupon break eight eggs, add a glass of wine, a glass of raisin wine and a little oil. Meanwhile grease a pan, place it on the hot ashes or in the hot bath in which pour the above described material; when the mixture is cooked in the double boiler, sprinkle it with ground pepper and serve.”
“Take roses fresh from the flower bed, strip off the leaves, remove the white from the petals and put them in the mortar; pour over some fish sauce and rub fine. Add a glass of fish sauce and strain the juice through the colander. This done, take four cooked calf’s brains, skin them and remove the nerves; crush eight scruples of pepper moistened with the juice and rub with the brains; thereupon break eight eggs, add a glass of wine, a glass of raisin wine and a little oil. Meanwhile grease a pan, place it on the hot ashes or in the hot bath in which pour the above described material; when the mixture is cooked in the double boiler, sprinkle it with ground pepper and serve.”
~ De re coquinaria (Apicius) Book 4, Chapter 2, ca. 5th century CE
I’m a big fan of eating brains.
My Roman ancestors felt the same way. The Roman cookbook Apicius contains recipes for brain sausages, brain-stuffed squash fritters and rose patina (patina de rosis), a baked dish of scrambled brain and eggs, flavored with roses.
Except among zombies and evil meteors, eating brains is far less popular globally than it once was. Modern science has found brains to be very high in cholesterol, and also tarnished their reputation by associating them with a deadly epidemic. That would be mad cow disease, properly known as bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). In the 1990s, a BSE outbreak in the UK caused a global panic, leading to the deaths of over 200 people and the slaughter of 4.4 million potentially-infected cattle.
Caused by the malfunctioning of DNA proteins called prions, BSE results in holes in the victim’s brain tissue (hence the name “spongiform”), leading to neural degeneration and death. It can be contracted from eating the meat and especially the brain of an infected animal, and transmission is unaffected by cooking. Which raises a reasonable question–didn’t the brain-craving Romans suffer from mad cow disease? Not exactly.
A Medieval copy of Digesta Artis Mulomedicinae, Vegetius’s guide to veterinary medicine. The prion disease of goats and sheep mentioned within might be scrapie, which was formally described by science in 1732. Photo by Sailko (2013).
BSE is not the only prion disease, and similar livestock illnesses are described by ancient writers such as Hippocrates in 400 BCE and Vegetius, who lived at the same time when Apicius was composed (4th and 5th centuries CE). But most prion diseases cannot pass from animal to human, making mad cow disturbingly unique. There is no ancient account of a person contracting a prion disease, although Hippocrates mistakenly conflated prion disease in animals with epilepsy in humans because of their similar symptoms.
BSE was first identified in 1986, and its development and spread were directly linked to the industrialization of 20th-century farming. Undesirable bits from slaughtered cattle, including their brains, were ground up and fed to living cattle as a protein supplement called MBM or “meat and bone meal”, inadvertently infecting the animals with prion disease (and giving me grisly flashbacks to Soylent Green and the “soap” from Cloud Atlas). Because of the ’90s BSE outbreak, most countries have banned the use of MBM in feed for ruminant (cud-chewing) animals such as cows and sheep, although it is still an ingredient in commercial pet food. As a further precaution, since prion diseases do not manifest until adulthood, it is now illegal in many countries to sell brain from an adult cow. Which is to say that this recipe, which uses calf brains, is just about as safe as it was in Roman times.
THE RECIPE
The sweet wine in the original Roman recipe, called passum, was made from raisins, making it a type of straw wine. Passum is still made in Italy today under the slightly-different name of passito. You can also use marsala, sherry, or Manischewitz.
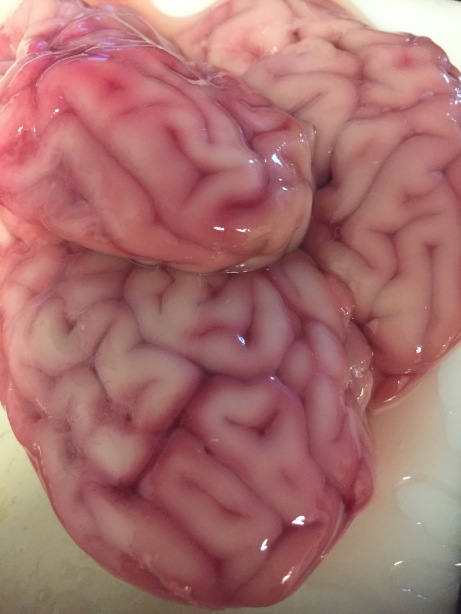
The main ingredient, looking exactly how you would expect.
Apicius provides some unusually specific instructions about incorporating roses into this dish: take fresh roses, “cut off the white” (presumably separate the petals from the flowerheads), grind with fish sauce and strain. I attempted this with fresh roses and their flavor/scent did not carry over into the fish sauce, so I ended up using rosewater (or rose tea), which I made by soaking dried rose petals in hot water.
-2 calf’s or pig’s brains (available, fresh or frozen, from halal butchers and some Mexican or Asian grocery stores)
-4 beaten eggs
-1/3 cup rosewater
-1/3 cup fish sauce
-1/2 cup sweet cooking wine
-1 teaspoon black pepper
-rose petals for serving (optional)
Rinse the brains in cold water and pat dry. Bring a small pot of water to a boil, lower the heat and simmer the brains until they are gray and a fork can pierce them easily (about 10 minutes).
In a blender or food processor, combine brains with all the other ingredients and blend until smooth. Pour the liquid into a pie dish greased with olive oil.
Apicius instructs the chef to cook the dish by placing it in termospodio, “in the embers.” You can use a double boiler to replicate the even, gentle heat of hot coals. I balanced my 9-inch pie dish on top of a cast-iron pan filled with water and added a lid.
Cook the patina over low heat for 40-45 minutes, until a fork inserted in the center comes out clean.
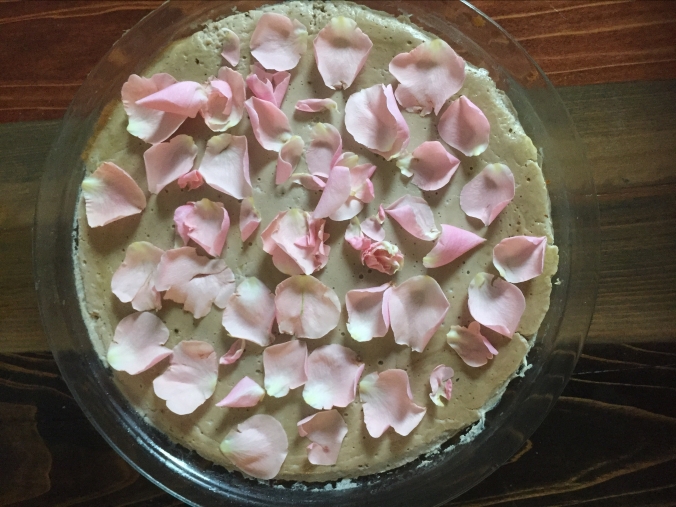
Serve with rose petals and more black pepper.
THE VERDICT
The flavor of brain resembles liver mousse, rich and creamy. The roses are an interesting addition, with a subtle flavor balanced by the sweetness of the wine. Like many baked Roman patinae, this one is soft and wet enough to require a spoon. Eat it by itself or with bread, while it’s still hot (nobody likes cold brains).

I suspect the “white part” referred to by Apicius is the portion at the base of the petal, right near where the petal would originally have been connected to the plant; you can see it on some of the petals you used to garnish the dish in the photographs above.
Kudos for your adventurous choice!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Pingback: Flower power – 3 mashed potatoes
Pingback: From Eggs to Apples Episode IV: Ancient Rome (Peach Patina with Cumin/Wine Sauce & Stuffed Dates) | Pass The Flamingo: Ancient Food History and Recipes